AS 90943 Investigate implications of heat for everyday life
I've never seen a cold penguin," ...... ornithologist Grant Ballard of the Point Reyes Bird Observatory.
I've never seen a cold penguin," ...... ornithologist Grant Ballard of the Point Reyes Bird Observatory.
Work for Friday....
|
We have the library ICT.
1 have a look at the youtube clip to the right 2 spend 10 minutes to try and find something that better explains heat transfer, if you do send me the URL via S Drive/science/dropbox 3 do the question on the sheet and hand it in |
|
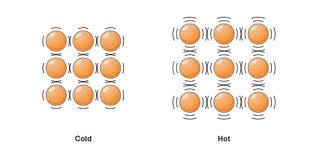
So... what is heat (and what is cold) ?
Does an iceblock have any heat?
Does an iceblock have any heat?
- Heat is a form of energy ........Click here for HMN notes
- It is a measure of the amount of movement of particles in an object
- So… it is the total kinetic energy
- It is measured in Joules
So... what is temperature?
- Temperature is the average speed (or kinetic energy) of the atoms for molecules in a substance. There are three different temperature scales: Celsius is the one we use
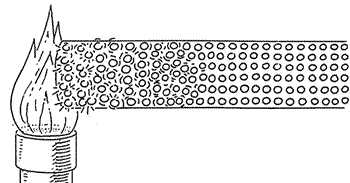
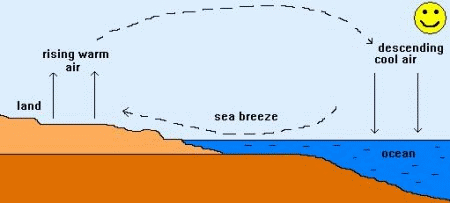
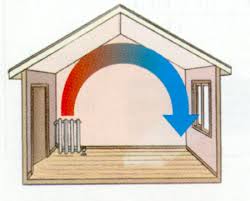
Heat transfer
There are 3 ways heat can be transferred or moved...
C......
C......
R......
There are 3 ways heat can be transferred or moved...
C......
C......
R......
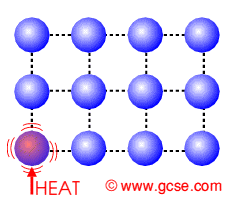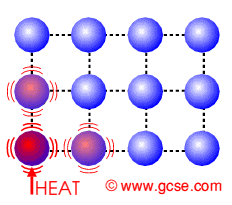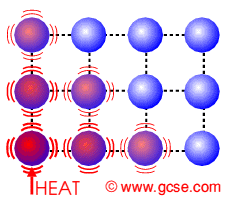
Firstly lets look at..... Conduction
How does HEAT ENERGY get transferred in a solid?
Describe what happens to the particles.
ie
Particles getting heated......
They ........ with their neighbours
causing their neighbours to.......
Thus heat energy......
Describe what happens to the particles.
ie
Particles getting heated......
They ........ with their neighbours
causing their neighbours to.......
Thus heat energy......
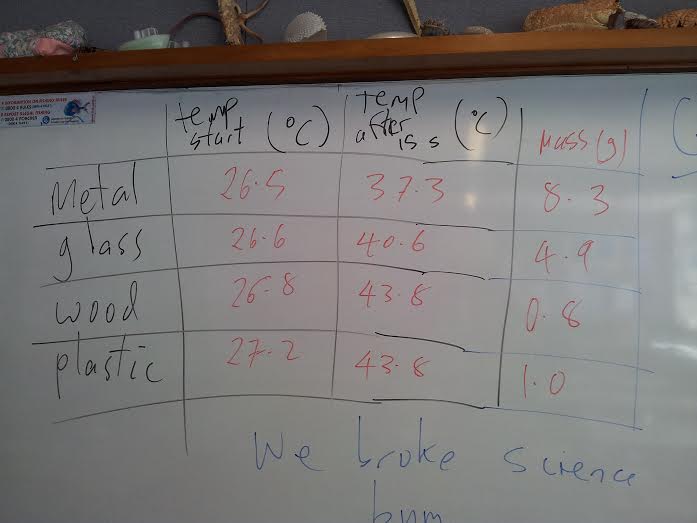
Did the metal get hottest in the 15 seconds of heating? .....hmmm seems not
But.... did it gain the most heat energy?
lets see....
the wood went up by 17 C , that is (17/15) = 1.1 C per second
calculating for every gram gives 1.1 x 0.8 = 0.9 C per gram for the wood
do this for the others... did we break science?
But.... did it gain the most heat energy?
lets see....
the wood went up by 17 C , that is (17/15) = 1.1 C per second
calculating for every gram gives 1.1 x 0.8 = 0.9 C per gram for the wood
do this for the others... did we break science?
|
Practice Question:
Two dishes were taken out of a HOT oven and placed on a cold bench. After 10 minutes I went to move them both, the metal one was fine to move but I got a nasty burn from the glass one. Explain that. You should include:
Hint.... remember SEXT |
Secondly lets look at..... Convection
The particles warm up and......
They take up more.....
They become less.....
So they.....
Thus heat energy......
They take up more.....
They become less.....
So they.....
Thus heat energy......
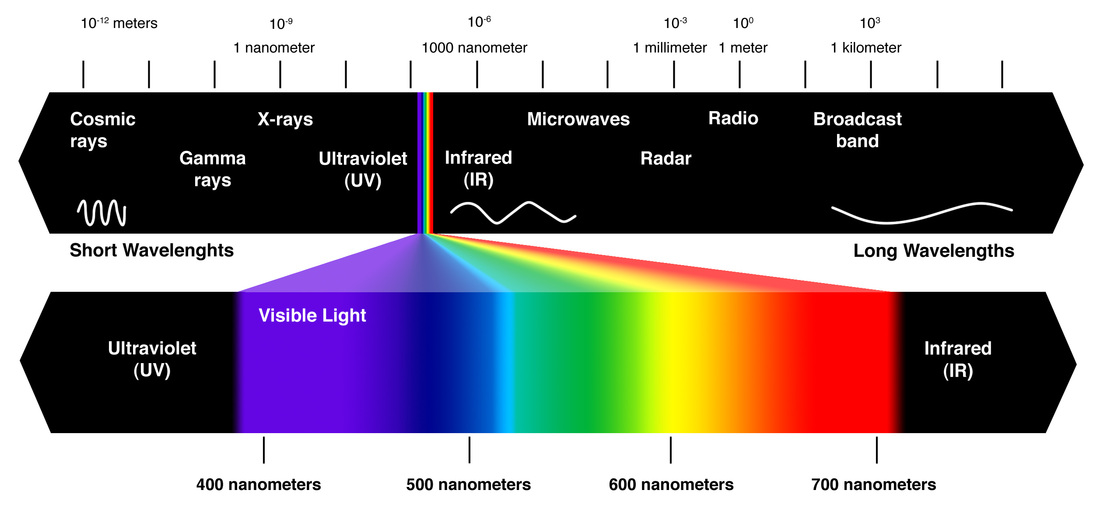
finally lets look at..... Radiation
Wikipedia says: Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change....
SAY WHAT?
lets go with this:
Radiation is....the transfer of energy via waves that can travel thru space (no particles are needed) Dark objects absorb solar radiation and heat up whereas light coloured objects reflect most of the radiation and do not heat up as much.
(look at your data sheet from our different coloured metals expt)
Wikipedia says: Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. When the temperature of the body is greater than absolute zero, interatomic collisions cause the kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules to change....
SAY WHAT?
lets go with this:
Radiation is....the transfer of energy via waves that can travel thru space (no particles are needed) Dark objects absorb solar radiation and heat up whereas light coloured objects reflect most of the radiation and do not heat up as much.
(look at your data sheet from our different coloured metals expt)
Overview video and quizz here
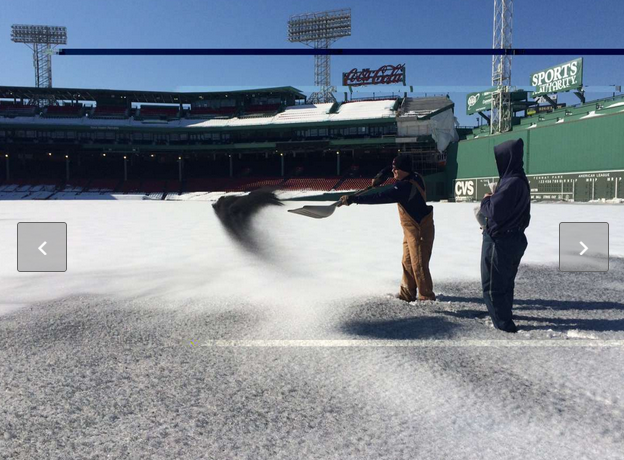
Black sand being used to melt snow.... (read article here)
Explanation: (relating to our primary data)
The black sand is absorbing solar radiation. Radiation is the transfer of energy via waves (electromagnetic), no particles are needed (unlike conduction and convection) so radiation can travel thru space.
Dark objects absorb solar radiation more than light objects- which reflect much of the radiation. This was shown in our expt (refer to your primary data) where the black coloured metal had an average temp increase of 12 degrees whereas the white metal had an average increase of only 3 degrees.
Therefore the black sand that is thrown over the snow is going to absorb more radiation than the white snow alone would, thus the sand heats up. This heated sand then melts the snow in the stadium... game on
Here is a thought... why is a thermos flask shiny silver on the inside?
Explanation: (relating to our primary data)
The black sand is absorbing solar radiation. Radiation is the transfer of energy via waves (electromagnetic), no particles are needed (unlike conduction and convection) so radiation can travel thru space.
Dark objects absorb solar radiation more than light objects- which reflect much of the radiation. This was shown in our expt (refer to your primary data) where the black coloured metal had an average temp increase of 12 degrees whereas the white metal had an average increase of only 3 degrees.
Therefore the black sand that is thrown over the snow is going to absorb more radiation than the white snow alone would, thus the sand heats up. This heated sand then melts the snow in the stadium... game on
Here is a thought... why is a thermos flask shiny silver on the inside?
Heat assessment
Definitions worksheet
Practice task: car
Practice tasks: hangi & igloo and hangi model answer helper (also below)
Practice tasks: Road and paraglider
Heating & cooling worksheet
Convection examples
Conduction examples
Heat questions
clips
igloo clip
Hangi helper
Radiation (question 1)
For this answer to count you need to be able to show your data from the expt in your booklet ... AND use it !!!
● Radiation is a type of heat transfer that doesn’t need ____________. Heat energy travels as waves and can travel through an empty _________.
● The colour of the surface affects whether the radiant energy is absorbed or ___________. My data showed me that a black surface will ___________ the most amount of radiant energy. The black metal increased __________. Other dark colours like blue and red were good absorbers of ___________ too.
● White and silver are poor absorbers and emitters of radiant energy. The white surface only increased by _______. White and Silver _______ radiant energy.
● The reason why the corrugated iron sheets are silver is because silver will ________ the radiant heat energy from the fire Therefore most of the heat energy is used to ______ the hangi stones rather than the sheets. If the metal had been black, red or blue the heat energy would have been ______ rather than reflected back to the fire. So this means the stones get ______
Convection and conduction (question 2)
● Convection is the type of heat transfer that happens in ______ and ______. Particles in a gas or liquid will start to move _______when heated. Particles that have gained energy and are moving faster will take up more_______ and becomes less ________. Less dense particles will_______ and be replaced by more dense particles. This is what we call a ____________ current.
● The food in the hangi is placed above the ______ stones. The food is getting cooked because of the convection current. The air particles and the steam particles down by the hot stones get heated by and become ____ ________ and rise. The rising particles will then transfer their energy to the _________ cooking it nicely.
● Conduction is a type of heat transfer that only happens in ________. The particles in a solid can vibrate but not move around freely. When a solid is heated the particles closest to the heat source will start to_______. They will then pass on the heat energy to the nearby particles as they ________ with them. ___________ do not have particles that are free to vibrate so much do not pass on heat energy as well as conductors.
The hangi has been insulated by placing dirt on top of the hole. The insulating soil prevents heat from ______ through the top of the hangi. Therfore the hangi stays hot and the kai cooks ka pai
Radiation (question 1)
For this answer to count you need to be able to show your data from the expt in your booklet ... AND use it !!!
● Radiation is a type of heat transfer that doesn’t need ____________. Heat energy travels as waves and can travel through an empty _________.
● The colour of the surface affects whether the radiant energy is absorbed or ___________. My data showed me that a black surface will ___________ the most amount of radiant energy. The black metal increased __________. Other dark colours like blue and red were good absorbers of ___________ too.
● White and silver are poor absorbers and emitters of radiant energy. The white surface only increased by _______. White and Silver _______ radiant energy.
● The reason why the corrugated iron sheets are silver is because silver will ________ the radiant heat energy from the fire Therefore most of the heat energy is used to ______ the hangi stones rather than the sheets. If the metal had been black, red or blue the heat energy would have been ______ rather than reflected back to the fire. So this means the stones get ______
Convection and conduction (question 2)
● Convection is the type of heat transfer that happens in ______ and ______. Particles in a gas or liquid will start to move _______when heated. Particles that have gained energy and are moving faster will take up more_______ and becomes less ________. Less dense particles will_______ and be replaced by more dense particles. This is what we call a ____________ current.
● The food in the hangi is placed above the ______ stones. The food is getting cooked because of the convection current. The air particles and the steam particles down by the hot stones get heated by and become ____ ________ and rise. The rising particles will then transfer their energy to the _________ cooking it nicely.
● Conduction is a type of heat transfer that only happens in ________. The particles in a solid can vibrate but not move around freely. When a solid is heated the particles closest to the heat source will start to_______. They will then pass on the heat energy to the nearby particles as they ________ with them. ___________ do not have particles that are free to vibrate so much do not pass on heat energy as well as conductors.
The hangi has been insulated by placing dirt on top of the hole. The insulating soil prevents heat from ______ through the top of the hangi. Therfore the hangi stays hot and the kai cooks ka pai